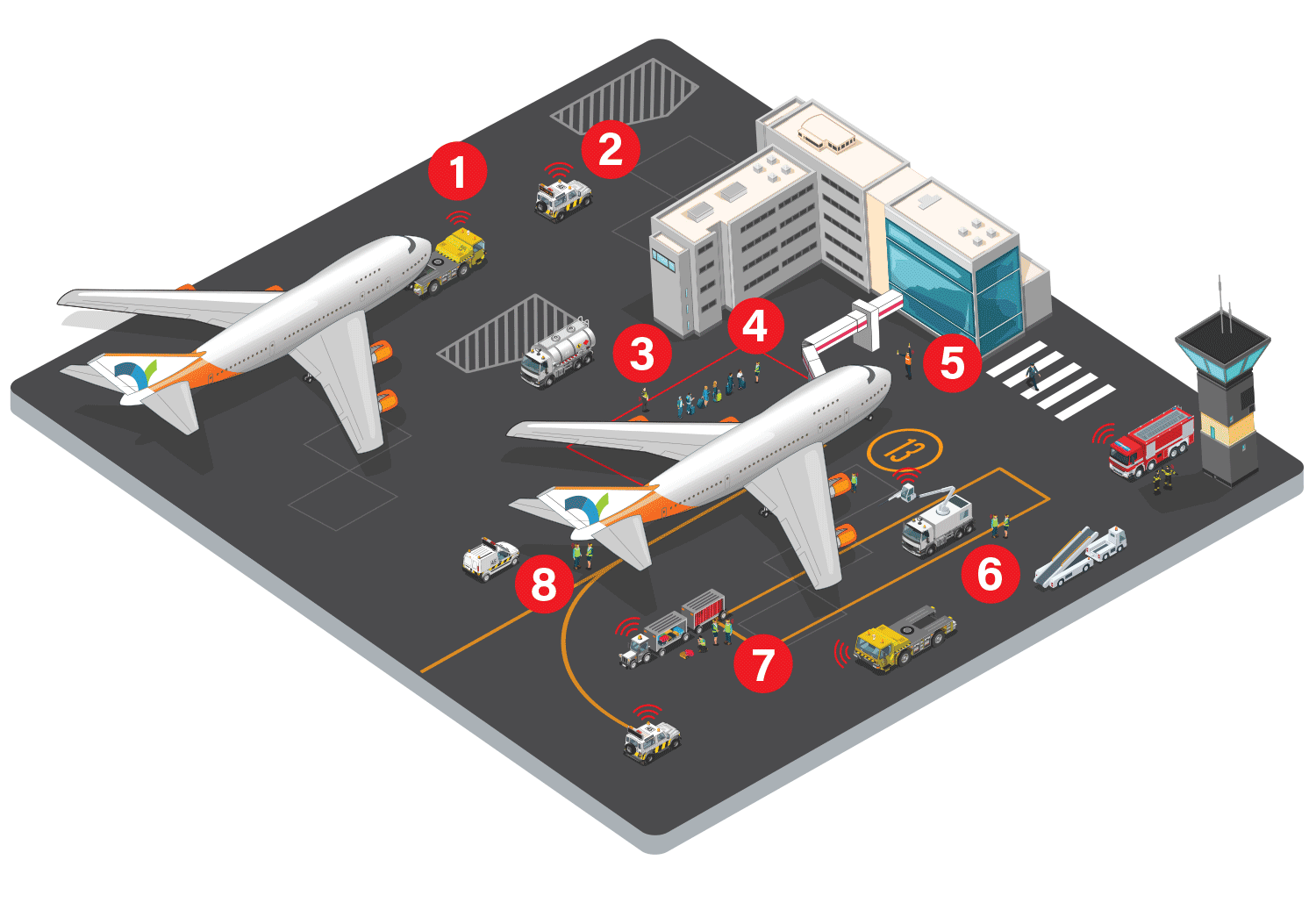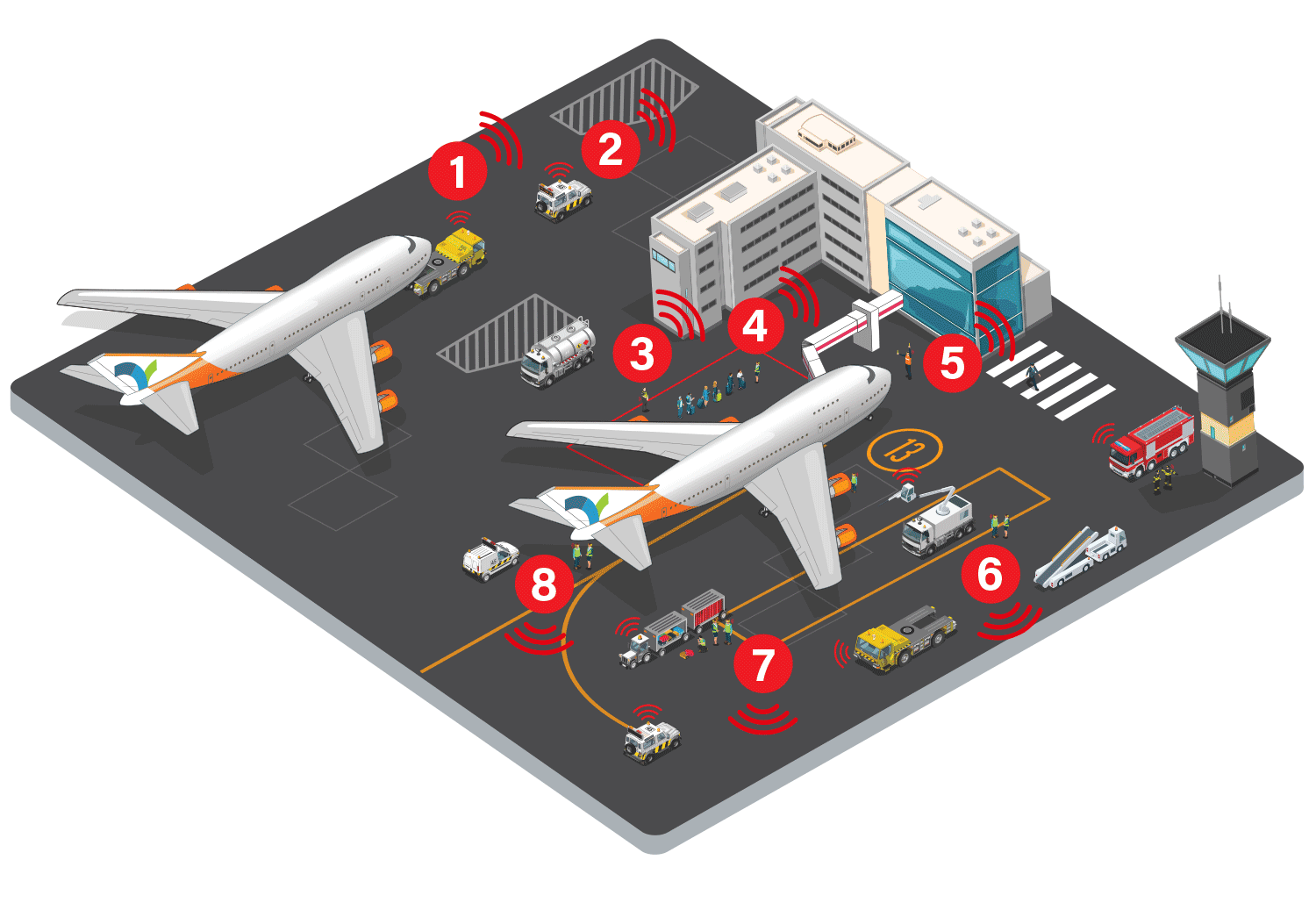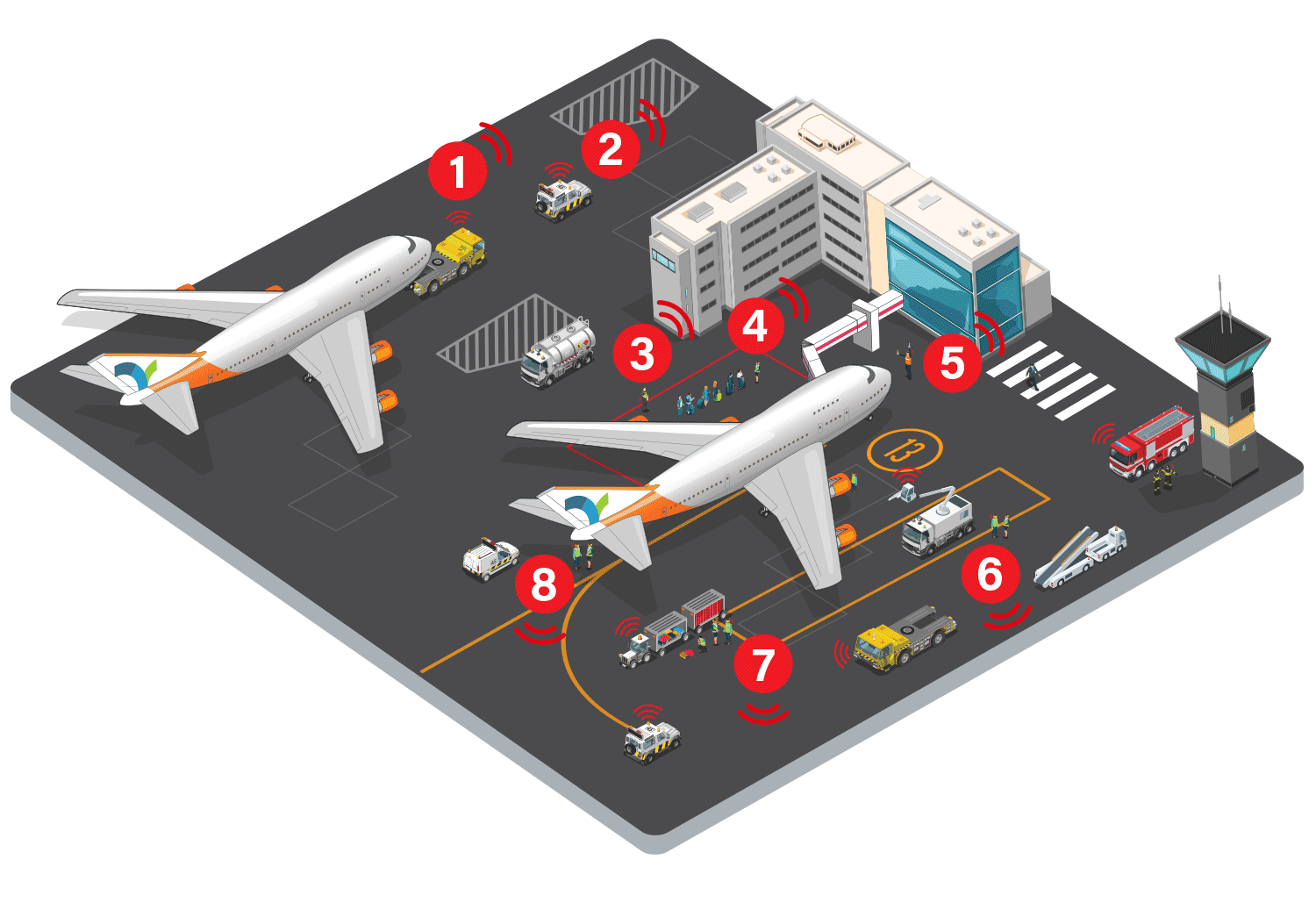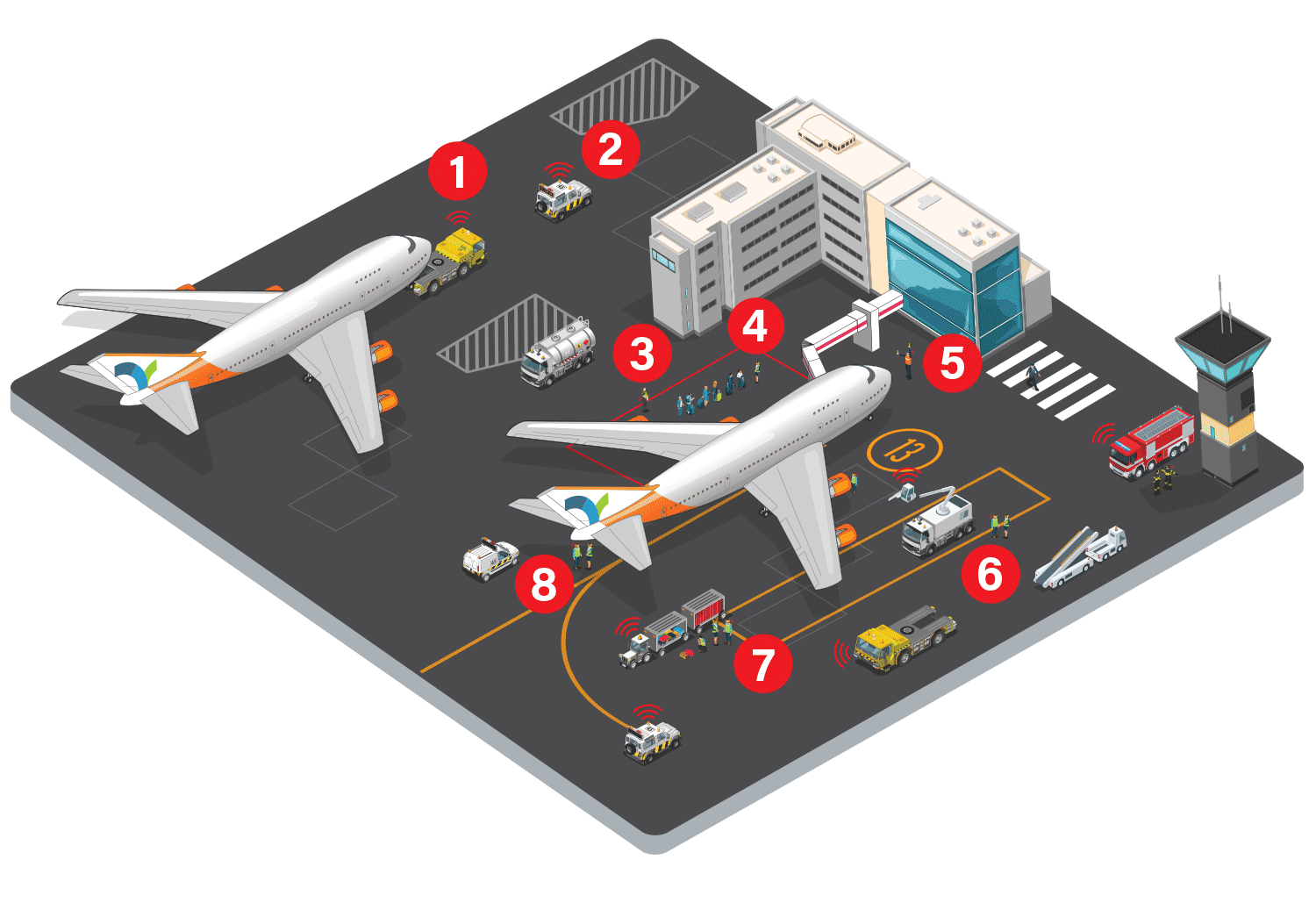
1. Ground to Air communications.

1. Ground to Air communications.
Ground crew members need to be able to communicate with the tower and aircraft crew during pushback and landing procedures. Airband radio systems enable all parties to exchange vital information about a wide range of topics, including tool and spare part preparation, fuel consumption, and requests for medical assistance.
2. On the move communication.

2. On the move communication.
Provided as a matter of convenience, or safety, or a combination of both, it is essential that ‘follow me’ airfield operational vehicles are connected to a central communications system.
DMR/TETRA radio systems allow for encrypted communication one to one, or one to a group, or to all on an emergency broadcast to connect with others such as security or fire teams.
Mobile units installed into vehicles with remote PTT buttons or foot switches allow for simple, easy to use communication whilst moving around airside.
3. Enhanced workplace safety.

3. Enhanced workplace safety.
During a recent AOA conference, it was revealed that 50% of incidents now occur as a result of manual handling, while the other 50% are attributed to slips, trips, and falls on the ramp.
To support safe inter-team communication, a DMR/BBPTT system can provide seamless communication for maintaining security on a manoeuvring area, teams loading cargo, or for individuals working at heights.
Furthermore, the system's man down feature and emergency button can instantly notify the team of any incidents or accidents, allowing them to request immediate assistance.
4. Robust, resilient communications.

4. Robust, resilient communications.
DMR/TETRA systems allow for encrypted communication one to one, or one to a group ensuring that ground services are carried out in a timely manner to meet the contracted KPI’s and protocols are followed during emergency situations. With traffic prioritisation capability an emergency broadcast can be made to connect with other users such as operations, security or fire teams.
Devices are deployed as hand portables, or mobile units installed into vehicles with remote PTT buttons or foot switches, allowing for simple, easy to use communication whilst moving around the apron.
5. Protection against high noise environments.

5. Protection against high noise environments.
Using heavy duty headsets (with VOX if required) can provide protection against high noise aviation environments by reducing the decibel level and preventing potential hearing damage.
Employees can engage in face-to-face conversations with colleagues without the need for shouting, while also ensuring clear communication through their headsets, two-way radios or Bluetooth-enabled devices, all while safeguarding their hearing. They also provide a line of communication to the pilots.
6. Telematics: integrated communications & tracking.
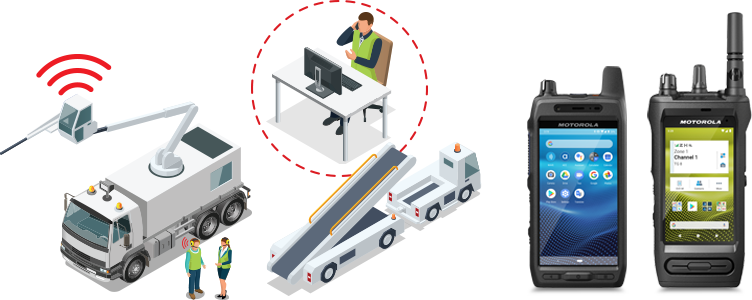
6. Telematics: integrated communications & tracking.
Telematic systems are designed to successfully live track and manage assets as they operate around an airport, supporting day-to-day operations.
- It offers the convenience of easily implementing geofencing for assets, which aids in operational efficiencies by tracking when equipment goes out of designated areas or enters restricted locations.
- The system enables driver-specific ID's, allowing for last known driver reporting and monitoring of driving performance, such as speeding or harsh braking.
- It helps keep track of the equipment in operation and available during a shift, providing valuable insights for resource planning.
- For added functionality, the system can be combined with in-vehicle cameras to view and record assets' movements on-site, making it an excellent tool for incident and accident management.
Examples of GSE equipment we can track
- Aircraft Chocks
- Lavatory servicing vehicles
- De-icing vehicles
- Baggage trucks
- Push back tugs
- Fuel bowsers
- Belt Loaders
- Tractors
- Lifters
- Engine stands
- Baggage dollies
- Portable water trucks
- Ground Power Units
- Boarding Steps
- Tripod Jacks
7. Photos and videos help resolve issues.
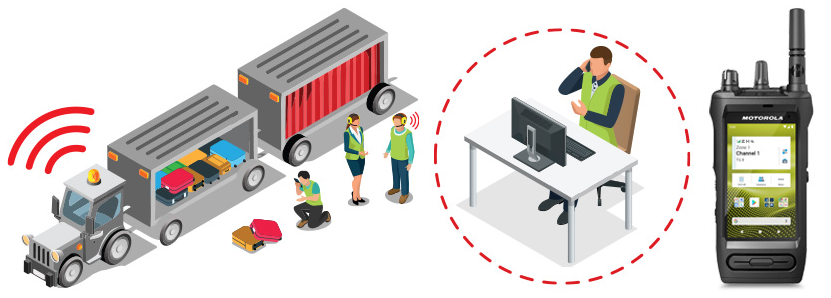
7. Photos and videos help resolve issues.
With the use of BBPTT smart devices and mobile apps, users have the capability to share visual content such as photos and videos. This also removes the need for employees to use their own personal device to share evidence.
Both the Duty Manager and any member of the team can comprehend the situation more effectively through visual evidence rather than relying solely on verbal explanations.
8. Co-ordinate responses.
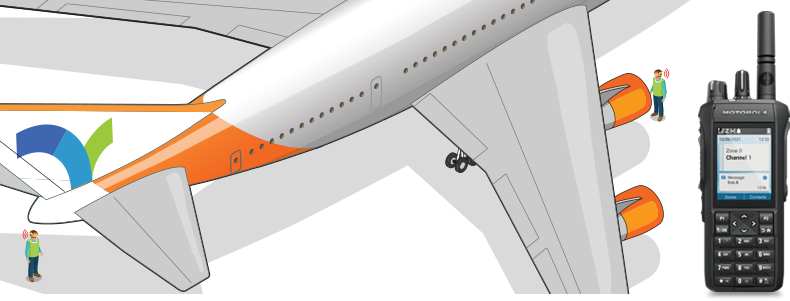
8. Co-ordinate responses.
When conducting an external check on an airport ramp, maintaining high levels of situational awareness is crucial for personal safety. It is important to always have a constant and careful lookout for potential hazards to prevent any accidents or injuries.
DMR radio communications equipment serves as an essential connection between the maintenance engineers at the front and back of the aircraft, ensuring effective co-ordination and enhancing overall safety, whilst also providing a connection to other users on the radio system to raise awareness of an issue or to call for assistance.